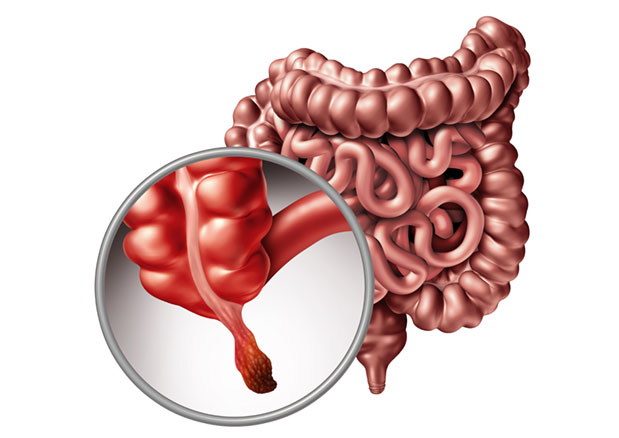
Appendicitis
WHAT CAUSES APPENDICITIS?
Some possible ways appendicitis could have developed include:
- Infection in the digestive tract, whether viral or bacterial in nature
- The tube joining the colon and the appendix becomes blocked by faeces
- Presence of tumour(s) in the area
WHAT YOU SHOULD LOOK OUT FOR
- A sharp, sudden pain located at the lower right side of the abdomen
- A sharp, sudden pain that starts from the navel and spreads into the lower right side of the abdomen
- Abdominal pain that worsens in intensity when coughing and walking
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Gassiness (flatulence) & bloating
- Constipation or diarrhoea
- Fever, especially as the infection worsens
ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A MEDICAL EMERGENCY
As acute appendicitis progresses very quickly; if left untreated, the inflamed and pus-filled appendix could rupture in as soon as 36 hours after symptoms appear.
When the appendix ruptures, it will release infected material into the abdominal cavity, which is a life-threatening emergency. If not treated in time, this can result in peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal lining), or sepsis – both of which can cause serious illness or even death.
To prevent such complications from developing, immediate surgery will be needed in order to remove the appendix and clean out the abdominal cavity thoroughly.
This is why seeking prompt medical attention upon the onset of symptoms is so important – so that one may have their inflamed appendix removed well before it potentially ruptures.
HOW IS IT TREATED?
The standard mode of treatment in most cases is to surgically drain the abscess. The procedure should not be painful as local or general anaesthesia will be used. Your doctor will advise you on the best course of action based on the severity of your condition, age and overall health.
To drain the abscess:
- Your doctor will make an incision on the abscess, allowing the pus to drain out
- Sometimes, a drain will be put in place to keep the incision open and draining
- Sometimes, the drained cavity is packed with gauze
- Drained abscesses are typically left open with no stitches required
If it is a deep abscess, overnight stay at the hospital may be needed for stronger pain relief and nursing care of the drainage.
Post-operative care typically includes:
- Take pain relief and/or antibiotics as prescribed
- Wash gently – let warm water run over the incision site daily, and pat dry
- Walk every day – this improves blood circulation and prevents constipation
- Stay hydrated so as to prevent constipation
Do remember to come back for your follow-up appointment so that your doctor can ensure that you are healing properly as intended.
APPENDICITIS SURGERY
Surgery to remove the appendix is known as an appendectomy, a very common emergency procedure and the standard of care for appendicitis. An appendectomy in Bangladesh may be done in two ways: open surgery or laparoscopic surgery.
Today, a laparoscopic appendectomy is more common, which offers eligible patients the advantages of smaller incisions, less post-operative pain, lower risk of complications and a faster recovery. In the hands of an experienced surgeon in Singapore, appendicitis surgery will prove to be a safe and efficacious one.
The primary treatment for appendicitis is the removal of the appendix – especially before it bursts. Rest assured that we are able to live well without an appendix.